Đề cương ôn tập học kỳ 2 môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 - Năm học 2018-2019 - Chương trình thí điểm
Bạn đang xem 20 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Đề cương ôn tập học kỳ 2 môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 8 - Năm học 2018-2019 - Chương trình thí điểm", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
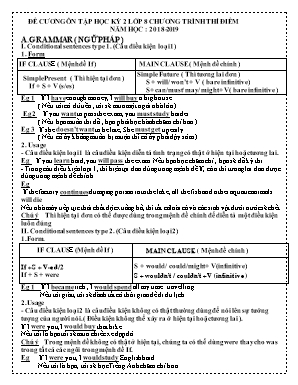
ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP HỌC KỲ 2 LỚP 8 CHƯƠNG TRÌNH THÍ ĐIỂM NĂM HỌC : 2018-2019 A.GRAMMAR ( NGỮ PHÁP ) I. Conditional sentences type 1. (Câu điều kiện loại 1) 1. Form IF CLAUSE ( Mệnh đề If ) MAIN CLAUSE ( Mệnh đề chính ) Simple Present ( Thì hiện tại đơn ) If + S + V (s/es) Simple Future ( Thì tương lai đơn ) S + will/ won’t + V ( bare infinitive ) S+ can/must/ may/ might+ V( bare infinitive ) Eg 1 If I have enough money, I will buy a big house. ( Nếu tôi có đủ tiền , tôi sẽ mua một ngôi nhà lớn ). Eg 2 If you want to pass the exam, you must study harder. ( Nếu bạn muốn thi đỗ , bạn phải học hành chăm chỉ hơn ). Eg 3 If she doesn’t want to be late, She must get up early. ( Nếu cô ấy không muốn bị muộn thì cô ấy phải dậy sớm ). 2. Usage - Câu điều kiện loại 1 là câu điều kiện diễn tả tình trạng có thật ở hiện tại hoặc tương lai. Eg If you learn hard, you will pass the exam. Nếu bạn học chăm chỉ , bạn sẽ đỗ kỳ thi. - Trong câu điều kiện loại 1, thì hiện tại đơn dùng trong mệnh đề If, còn thì tương lai đơn được dùng trong mệnh đề chính. Eg If the factory continues dumping poison into the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals will die Nếu nhà máy tiếp tục thải chất độc xuống hồ, thì tất cảloài cá và các sinh vật dưới nước sẽ chết. Chú ý Thì hiện tại đơn có thể được dùng trong mệnh đề chính để diễn tả một điều kiện luôn đúng II. Conditional sentences type 2. (Câu điều kiện loại 2) 1.Form. IF CLAUSE (Mệnh đề If ) MAIN CLAUSE ( Mệnh đề chính ) If +S + V-ed/2 If + S + were S + would / could/might + V(infinitive) S + wouldn’t / couldn’t +V (infinitive) Eg 1 If I became rich , I would spend all my time travelling. Nếu tôi giàu, tôi sẽ dành tất cả thời gian để đi du lịch. 2.Usage - Câu điều kiện loại 2 là câu điều kiện không có thật thường dùng để nói lên sự tưởng tượng của người nói. ( Điều kiện không thể xảy ra ở hiện tại hoặc tương lai ). If I were you, I would buy that bike. Nếu tôi là bạn tôi sẽ mua chiếc xe đạp đó. Chú ý Trong mệnh đề không có thật ở hiện tại, chúng ta có thể dùng were thay cho was trong tất cả các ngôi trong mệnh đề If. Eg If I were you, I would study English hard. Nếu tôi là bạn, tôi sẽ học Tiếng Anh chăm chỉ hơn. III. The Present Simple (Thì Hiện tại đơn ) 1. Form. (Cấu trúc) a. Positive (Câu Khẳng định) I / We / You / They + V( nguyên mẫu) He / She / It + V (s/es) Eg I go to school every day. My father often watches TV at 7 p.m b. Negative (Câu Phủ định) I / We / You / They don't (do not)+ V (nguyên mẫu) He/ She / It doesn't (does not) + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg I don’t go to school on Sundays. He doesn’t play games on Saturdays. c. Question (Câu nghi vấn) Do I / We / You / They + V (nguyên mẫu) Does He/ She / It + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg Do you go to school every day ? Does he play football every afternoon? 2. Usage (Cách dùng) - Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả thói quen hằng ngày. Eg He gets up at 5 o’clock in the morning. -Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả sự việc hay sự thật hiển nhiên. Eg We have two children. -Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả sự việc xảy ra trong tương lai theo thời gian biểu hay lịch trình. Eg The plane takes off at 5.00 tomorrow morning. + Các trạng từ đi kèm với thì hiện tại đơn Every day / week / month..(Hằng ngày / tuần / tháng...) Always : luôn luôn Usually : thường xuyên Often : thường Sometimes : thỉnh thoảng Seldom : hiếm khi Never : không bao giờ NOTE (CHÚ Ý) Những động từ tận cùng là : o, s , ch , sh, x, z , ta thêm es Eg go -> goes watch -> watches wash -> washes fix -> fixes - Những động từ tận cùng là y mà đằng trước là nguyên âm ( u, e ,o , a, i) ta để nguyên y rồi thêm s Eg play -> plays say -> says Những động từ tận cùng là y mà đằng trước là phụ âm ta đổi y thành i rồi thêm es Eg study -> studies fly -> flies IV. The Present Continuous (Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn) 1. Form (Cấu trúc) a. Câu khẳng định I + am + V-ing He / She / It + is + V-ing We / You / They + are + V-ing Eg I am learning English at the moment. He is playing football now. We are listening to music at this time b. Câu phủ định I + am + not + V-ing He / She / It + is + not + V-ing We / You / They + are + not + V-ing Eg I am not learning English at the moment. He is not playing football now. c. Câu nghi vấn. Am + I + V-ing Is + He / She / It + V-ing Are + You / We / They + V-ing Eg Are you learning English at the moment? Is He playing football now ? 2. Usage. (Cách dùng) -Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn dùng để diễn tả một hành động đang xảy ra tại thời điểm nói trong hiện tại. Eg She is talking to her teacher about that plan. - Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn đề cập đến những thói quen xấu gây khó chịu cho người khác, thường đi cùng trạng từ “ always “ hoặc “constantly”. Eg He is always leaving his dirty socks on the floor. - Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn dùng để diễn tả những tình huống đang thay đổi. Eg Her son is getting better. -Thì hiện tại tiếp diễn diễn tả một kế hoạch chắc chắn sẽ xảy ra trong tương lai (thường đi cùng với trạng từ chỉ thời gian trong tương lai). Eg. I am studying English next summer. Các trạng từ đi kèm với thì hiện tại tiếp diễn. Now : bây giờ At the moment : ngay bây giờ At this time : vào lúc này Today : hôm nay Be quiet : Hãy yên lặng Listen : Nghe này V. The Present Perfect (Hiện tại hoàn thành) 1. Form (Cấu trúc) a. Câu khẳng định I /You/ We/ They + have + Ved / Vpp He / She / It + has + Ved /Vpp Eg I have lived in Thanh Hoa city since 1987 He has bought a new car for 2 weeks. b. Câu phủ định I /You/ We/ They + have + not + Ved / Vpp He / She / It + has + not + Ved /Vpp Eg I haven’t lived in Thanh Hoa city since 1987 He hasn’t bought a new car for 2 weeks. c. Câu nghi vấn Have + I /You/ We/ They + Ved / Vpp Has + He / She / It + Ved /Vpp Eg Have you been to England ? Has Ba gone to Sam Son beach? 2. Usage (Cách dùng). - Thì hiện tại hoàn thành diễn tả sự việc xảy ra trong quá khứ và kéo dài đến hiện tại. Eg I have learnt English for 15 years. She has lived here since 2016 - Thì hiện tại hoàn thành diễn tả sự việc vừa mới xảy ra nhưng không đề cập đến thời gian ,thường dùng với các từ như “ just, already hay yet. Eg She has just come. They haven’t arrived yet. -Thì hiện tại hoàn thành dùng để nói về các sự việc vừa mới xảy ra và hậu quả của nó vẫn còn ảnh hưởng đến hiện tại. Eg He has just washed his car, so it looks very clean now. -Thì hiện tại hoàn thành khi nói về trải nghiệm hay kinh nghiệm , thường đi kèm với ever/ never. Eg Have you ever been to London ? I have never seen that movie before. Những trạng từ chỉ thời gian đi kèm với thì hiện tại hoàn thành: Ever : bao giờ Never : không bao giờ So far : cho đến bây giờ / nay Serveral times : vài lần rồi Just : vừa mới’ Already : rồi Yet : chưa VI. The present simple for future.( Thì hiện tại đơn mang ý nghĩa tương lai) 1. Form. (Cấu trúc) a. Positive (Câu Khẳng định) I / We / You / They + V( nguyên mẫu) He / She / It + V (s/es) Eg I go to school every day. My father often watches TV at 7 p.m b. Negative (Câu Phủ định) I / We / You / They don't (do not)+ V (nguyên mẫu) He/ She / It doesn't (does not) + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg I don’t go to school on Sundays. He doesn’t play games on Saturdays. c. Question (Câu nghi vấn) Do I / We / You / They + V (nguyên mẫu) Does He/ She / It + V (nguyên mẫu) Eg Do you go to school every day ? Does he play football every afternoon? 2. Usage (Cách dùng) - Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả thói quen hằng ngày. Eg He gets up at 5 o’clock in the morning. -Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả sự việc hay sự thật hiển nhiên. Eg We have two children. Ngoài cách dùng ở trên , thì hiện tại đơn còn mang ý nghĩa tương lai khi nói về thời gian biểu, chương trình , lịch trình , và trong các trạng từ chỉ thời gian cụ thể.. Eg The plane takes off at 5.00 tomorrow morning. VII .The past perfect .( Thì quá khứ hoàn thành ) 1.Form a) Thể khẳng định (Affirmative form) S + had + p.p Eg: I had left my wallet at home. b) Thể phủ định (Negative form) s + hadn’t + p.p Eg: The house was dirty. They hadn’t cleaned it for weeks. c) Thể nghi vấn (Interrogative form} Had + s + p.p? Eg: Where had he put his wallet? 2. Cách dùng: Thì quá khứ hoàn thành được dùng để diễn tả: a) Hành động hoặc trạng thái đã xảy ra và đã kết thúc trước một thời điểm trong quá khứ. By the end of last semester, we had finished Book IV. Cuối học kỳ trước, chúng ta đã hoàn thành quyển 4. Before his mother came back, he had tidied up the whole room. b) Hành động đã xảy ra và kết thúc trước một hành động quá khứ khác (hành động xảy ra trước dùng quá khứ hoàn thành, hành động xảy ra sau dùng quá khứ đơn). I had seen him before he saw me. c) Hành động đã xảy ra và kéo dài đến một thời điểm nào đó trong quá khứ. Ex: By nine o'clock, we had studied for three hours in the classroom. Chúng tôi đã học 3 tiếng đồng hồ trong lớp từ lúc 9 giờ. I had worked for several hours when he called. She told me that she had walked for two hours. *** LƯU Ý: Dấu hiệu nhận biết: Trong câu thường có các từ: before(TRƯỚC KHI ), after(sau khi), when(khi), by the time(vào thời điểm), by the end of + time in the past Ex: *When I got up this morning, my father had already left. * By the time S. Past, Past Perfect. By the time I met you, I had worked in that company for five years. * S. Past After Past Perfect They went home after they had eaten a big roasted chicken. (Họ về nhà sau khi đã ăn một con gà quay lớn.) After I had bought a new pen, I found my pen * Past Perfect Before S.past She had done her homework before her mother asked her to do so. Before he arrived his office, his secretary had gone out IX. PASSIVE VOICE (THỂ BỊ ĐỘNG) CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG (Passive sentences): Câu bị động là câu trong đó chủ ngữ là người hay vật nhận hoặc chịu tác động của hành động. Eg: (A) I asked a question. →(P) : A question was asked by me. Một câu hỏi được hỏi bởi tôi. B. Cách chuyển từ câu chủ động sang câu bị động: * Thể khẳng định (Affirmative form) S + be + p.p (Past Participle) + (by + 0) Ex: The picture was painted by Tom. S be + p.p O * Thể phủ định (Negative form) S + be not + p.p + (by + 0) Ex: The picture was not painted by Tom. s be + p.p o * Thể nghi vấn (Interrogative form) Be + S + p.p + (by + 0)? Ex: Was the picture painted by Tom? Be S p.p o Động từ be ở đây phải phù hợp với chủ ngữ cũng phải thể hiện được thì cuar câu. Khi dịch nghĩa câu bị động, ta dịch là “bị, được” tùy vào câu, ngữ cảnh mà ta chọn nghĩa cho phù hợp. Câu bị động ở từng thì: TENSES (Các loại thì) PASSIVES STRUCTURE(Cấu trúc bị động) Present simple (Hiện tại đơn ) I learn English. is/ are/ am + V.pp / Ved English is learned (by me). Present progressive ( QK Tiếp Diễn) She is reading the book. is/ are/ am + being + V.pp / V.ed The book is being read (by her). Past simple ( Quá khứ đơn) The little boy broke the glass. was / were + Vpp / Ved The glass was broken by the little boy. Past progressive ( QK Tiếp Diễn) The police were interrogating him. was/ were + being + V.pp / Ved He was being interrogated by the police. Present perfect ( QK hoàn thành) She has cooked the food. have/ has been + V.pp / Ved The food has been cooked (by her). Future simple ( Tương lai tiếp diễn ) They will cover the road with a red carpet tomorrow. will be + V.pp / Ved The road will be covered with a red carpet tomorrow. Future progressive I will be holding the wedding party ưi Ha. Noi next month. will be being + V.pp / Ved My wedding party will be being held in Ha Noi next month. X. Future continuous .( THÌ TƯƠNG LAI TIẾP DIỄN) 1.Form (+) S + will/ shall + be + V-ing Ex: I / we shall be working You / he, she , it, they will be + working (-) S + won’t / shan’t + be + V-ing Ex: I / we shan’t be working You / he, she , it, they won’t be + working (?) Shall + S + be + V-ing? Ex: Shall I / We + be working? Will you/ he/ she /it / they be working? 2.Usage: Thì tương lai tiếp diễn được dùng để: - .Diễn tả một hành động kéo dài trong một thời gian nào đó ở tương lai Ex: By this time torromow, They will be playing volleyball - .Diễn tả một hành động sẽ xảy ra trong tương lai mà thời điểm không cần xác định ex:I’ll be visting her tomorrow XI. Verb to –Infinitive Nếu chúng ta muốn tuân theo một động từ với một hành động khác , chúng ta phải sử dụng một danh động từ hoặc một động tử (to infinitive) Verb + to-infinitive ( V + to V) Ex: I want to go to the market. - Một số động từ thông thường tuân theo bởi to – Ininitive Choose, decide, plan, love, hate, prefer, try, want , need * Note:một số động từ như: love, hate, prefer có thể tuân theo cả hai : V-ing và to – V mà không đổi nghĩa XII. QUY TẮC ĐÁNH DẤU TRỌNG ÂM 1.Đánh dấu nhấn âm trên từ có âm kết thúc là -ic và -al *Khi thêm một hậu tố -ic vào một từ thì sẽ làm từ đó thay đổi cách nhấn âm. Ta sẽ nhấn âm trước ngay hậu tố thêm vào. Hay nói cách khác ta sẽ nhấn âm ngay trước hậu tố -ic của một từ. Ex: atom —► a’tomic; po' etic *Khi thêm một hậu tố -al vào một từ thì sẽ không làm thay đổi cách nhấn âm của từ đó. Ex: 'music —> 'musical Lưu ý: Nếu một từ có thể dùng cả hai hậu tố: một hậu tố là -ic và một hậu tố khác là -al, thì giữa hai từ này có cùng một cách nhấn âm.: Ex: e'conomy —► economic —> economical botanic —► bo'tanic —► bo’tanical 2. Các từ có tận cùng là: -ese, -ee, -eer, -oo, -oon, -ique, -ed, -esque thì trọng âm rơi vào những từ này: Ex. Vietna'mese, employ'ee, adop’tee, addre’ssee, intervi’ew, Cantonese, Taiwan’ese 3. Những từ có 3 âm tiết trở lên thì trọng âm (nhấn âm) rơi vào âm tiết thứ ba từ phải sang trái. Ex: ge'ography Chú ý: Đối với từ mà tận cùng -logy và – graphy thì dấu nhấn được nhấn vào âm thứ ba kể từ cuối trở lên. Technology—►Technology Biology —► bi'ology geography—►ge'ography photography —►pho'tography apology —►a'pology ecology —► e'cology 4. Những từ tận cùng là -ity and -itive Những từ có tận cùng là-ity and -itive , thì trọng âm đứng trước hậu tố Ex: ‘possitive, oppor’tunity. XIII. CAUSE VÀ EFFECT Cause Effect 1. Because /Since + Clause Ex: Because the water is polluted, the fish are dead. so + clause Ex: The water is polluted, so the fish are dead 2. Due to /because of + sthing Ex: The fish is dead because of the pulluted water. to cause sth / to lead to sth/ to result in sth Ex: The polluted water, causes/ resukt in the death of fish. to make sbody/sth do sth Ex: the poluted water makes the fish die . QUY TẮC CHUYỂN TỪ "BECAUSE" SANG "BECAUSE OF". Nhìn phía sau Because (câu đề) thấy có "there, to be" thì bỏ. TH1: Nếu thấy 2 chủ ngữ giống nhau thì bỏ chủ ngữ gần Because, động từ thêm "ing". Ví dụ: Because Nam is tall, he can reach the book on the shelf. => Because of being tall, Nam can reach the book on the shelf. TH2: Nếu thấy chỉ còn lại danh từ thì chỉ việc giữ lại danh từ mà dùng. Ví dụ: Because there was a storm, ... => Because of the storm, ... - Sau khi bỏ "there", bỏ "to be" (was) chỉ còn lại danh từ => chỉ việc lấy mà dùng. TH3: Nếu thấy có danh từ và tính từ thì đưa tính từ lên trước danh từ, còn lại bỏ hết. Ví dụ: Because the wind is strong, ... => Because of the strong wind, ... - Sau khi bỏ "to be" (is) thấy có danh từ và tính từ nên ta chỉ việc đưa tính từ lên trước danh từ. TH4: Nếu thấy chỉ có mình tính từ => đổi nó thành danh từ Ví dụ: Because it is windy, ... => Because of the wind, ... TH5: Nếu thấy có sở hữu lẫn nhau => Dùng danh từ dạng sở hữu Ví dụ: Because I was sad, .... => Because of my sadness, ... Ví dụ: Because he acted badly, ... => Because of his bad action, ... (trạng từ đổi thành tính từ) - Trong 2 ví dụ trên ta thấy có sự sở hữu: I + said => my sadness; he + act => his action nên ta dùng sở hữu. Nếu có trạng từ các em nhớ chuyển nó thành tính từ. B.EXERCISE (BÀI TẬP) VOCABURLARY AND GRAMMAR Question I. Choose the best answer. (A,B, C or D ) 1. I like ______________ back my home village on holiday. A. comes B. come C. came D. coming 2. If the factory ________________ dumping poison into the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals will die. A. continues B. to continue C. continued D. will continue 3.Water ________________ in the lake has made the fish die. A. pollution B. pollute C. polluted D. polluting 4. Mi and Nick like ______________ back Mi’s home village on holiday. A. comes B. come C. came D. coming 5. If the factory continues dumping poison into the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals ________________. A. die B. to die C. dead D. will die 6. Water pollution is the ________________ in the lake has made the fish die. A. contaminating B. contaminate C. contaminated D. contamination 7. If we ______________ water carefully, more people will have fresh water. A. will use B. would use C. using D. use 8. If the factory continues dumping poison ________________ the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals will die. A. into B. to C. about D. in Question II. Choose the best answer. (A,B, C or D ) 1. Mi and Nick like ______________ back Mi’s home village on holiday. A. comes B. come C. came D. coming 2. If the factory ________________ dumping poison into the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals will die. A. continues B. to continue C. continued D. will continue 3.Water ________________ in the lake has made the fish die. A. pollution B. pollute C. polluted D. polluting 4.If the air wasn’t dirty, I ________________ so much. A. wouldn’t sneeze B. sneeze C. would sneeze D. to sneeze 5. If the factory continues dumping poison into the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals ________________. A. die B. to died C. dead D. will died 6. Water pollution is the ________________ in the lake has made the fish die. A. contaminating B. contaminate C. contaminated D. contamination 7. If I were you , I ______________ that car . A. would buy B. buy C. bought D. buying 8. If we recycle more , we ________________ the Earth. A. help B. would help C. helping D. will help Conditional Sentence Type I : Câu điều kiện loại 1 Question I. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form. (Chia những động từ trong ngoặc đơn vào đúng hình thức). 1.If we (recycle) ________ more, we will help the Earth. 2. Factories (not dump) ______________waste into rivers if the government fine them heavily. 3. If people travel to work by bus, there (be) ______________fewer car fumes. 4. We (save) ________________thousands of trees if we don’t waste paper. 5. If we use water carefully, more people (have) ______________fresh water. 6. If the factory ( continue) ________________ dumping poison into the lake, all the fish and other aquatic animals will die. 7.If we recycle more, we (help) ________________ the Earth. 8. If people (travel)________________to work by bus, there will be fewer car fumes. 9. We save thousands of trees if we (not waste)_______________don’t waste paper. 10. Factories don’t dump waste into rivers if the government ( fine) _______________ them heavily. Question II. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form. (Chia những động từ trong ngoặc đơn vào đúng hình thức). 1. If he (study) ________________ harder, he can pass an exam. 2. She may be late if she (not hurry) ________________. 3.If you study harder, you (pass) ________________ the exam. 4. If you are kind to me, I (be) _______________ good to you. 5.If he (give) _______________ up smoking, as his doctor orders, he will be soon well again. 6. You (not pass) _______________ your driving test unless you drive more carefully. 7. He’ll be ill if he (not stop) ________________ worrying so much. 8. We’ll go to the beach tomorrow if it ( be) ________________ nice. Question III.Combine each pair of sentences to make a conditional sentence type 1. (Kết hợp mỗi cặp câu sau để tạo thành câu điều kiện loại 1) 1.Students are more aware of protecting the environment. Teachers teach environmental issues at school. If 2.Light pollution happens. Animals change their behaviour patterns. If .. 3.The levels of radioactive polluion decrease.We switch from nuclear power to renewable energy sources. If .. 4.The water temperature increases.Some aquatic creatures are unable to reproduces. If..................... 5.People get more diseases.The water is contaminated. If Conditional Sentence Type II : Câu điều kiện loại 2 Question IV. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct form. (Chia những động từ trong ngoặc đơn vào đúng hình thức). 1. If I were you, I (look) ________________ for a new place to live. 2. If Lan wasn’t ill, she ( join) ________________ out tree planting activity. 3.If there were fewer cars on the road, there (be) ________________ less pollution. 4.If people really cared about the environment, they ( not dump ) ________________ waste into the lake. 5.If there was no fresh water in the world, what (happen) ________________. 6.If you (be) ________________ the president, what would you do to help the environment ? 7.They get sick so often.If they exercised more, they (be) ________________ heathier. 8.If I (have) ________________ one million US dollars , I would build more parks in our city. 9.Quan’s mother is unhappy.If Quan tided his room every day, his mother (not be) __________ so upset. 10.There isn’t a garden at house .If there were, we (grow) ________________ vegetables. Question V.Write a conditional sentence type 2 for each situation, as in the example. Viết loại câu điều kiện loại 2 cho mỗi tình huống , như trong ví dụ. 1.People throw rubbish in the street.The street doesn’t look attractive. If people didn’t throw rubbish in the street, it would look attractive. 2.There are so many billboards in our city. People can not enjoy the view. If . 3.There is so much light in the cityat night.We can not see the stars clearly. If 4.We turn on the heater all the time. We have to pay three million dong for electricity a month. If 5.The karaoke bar makes so much noise almost every night. The residents complain to its owner. If 6.She has a headache after work every day.She works in a noisy office. If . C.READING Question I Read the passage and choose the correct answer A, B, C or D. Environmental pollution is a term that (1)______ to all the ways by which man pollutes his surroundings. Man dirties the air with (2)______ gases and smoke, (3)_____ the water with chemicals and other substances, and damages the (4)_____ with too many fertilizers and pesticides. Man also pollutes his surroundings (5)_____ various other ways. For example, people ruin natural beauty by (6)_____ junk and litter on the land and in the water. Environmental pollution is one of the most serious problems facing mankind today. Air, water and soil are necessary to the (7)_____ of all living things. Badly polluted air can cause illness, and (8)_____ death. Polluted water kills fish and other (9)_____ life. Pollution of soil reduces the amount of land that is available for growing food. Environmental pollution also brings ugliness to man’s (10)_____ beautiful world. 1. A. means B. refers C. provides D. reduces 2. A. thick B. natural C. exhaust D. influent 3. A. purifies B. pumps C. sprays D. poisons 4. A. soil B. forests C. streets D. beaches 5. A. on B. in C. by D. with 6. A. spoiling B. leaving C. scattering D. gathering 7. A. survival B. environment C. development D. growth 8. A. so B. ever C. too D. even 9. A. animal B. marine C. human D. plant 10. A. nature B. natural C. naturally D. natured Question II Read the passage and answer the questions. Visual pollution has a greater effect on people than you may think. I remember when I went to a big city, I was really scared because so much graffiti on the buildings' wall. Then I looked up, and I saw a lot of power lines over my head. Although they were not dangerous, I still felt unsafe since I thought they might fall down. These things prevented me from enjoying the beautiful sights of the city. I also remember the time when I was a student at a university. Once I was so busy with my assignments that I did not tidy my room for two weeks. Looking at the messy room caused me so much stress that I did not want to study. Then I decided to clean the room and put my thing in their proper places. I also bought a small plants and placed it in a corner of the room. These simple actions increased my motivation and helped me to focus on my learning. Questions. 1.How did the author feel when she saw the power lines? . 2.Why did she have that feeling? 3. What was she busy with? 4. What happened when she looked the messy room? 5. What did she do for her room? V. Supply the correct tense of the verbs given in each blanket. Four countries ______________ (visit) by John so far. London ______________ (have) a population of eight million people. The Statue of Liberty in New York is a monument which ______________ (symbolize) freedom. Vietnam’s Independence Day ________________ (celebrate) on September 09th. We ______________ (visit) Sydney Opera House for several times. Some activities ______________ (prepare) to celebrate the lunar new year now. Ex2: Put the verbs in the brackets in the correct form of tense. 1. My uncle (just open) a new internet shop on Trang Tien street. 2. .Linh (watch) ...TV at 9 o’clock last night? 3. While Mr Brown (work)..... in the garden, his wife (cook) 4. Nam (not buy).. a new computer since he (sell). the old one last month. 5. Mr Phong (go) .to New York for ten days last year? 6. Last year we (install) ordinary light bulbs, but now we (use) new ones. 7. When I (arrive).... at her house yesterday, she (do) ..her homework. 8. He (be) ...very successful in his business since he (come) ....here . 9. That exercise can’t (do) by all the students. 10. His car (repair) at this time yesterday. 11. This room (clean) by my sister every day. 12. ...these toys (make) in China? 13. These story books (write) .. by To Hoai in 1956. 14. Nam (award) a gold medal in the chess tournament last week. 15. Nothing (do).... since Peter bought a computer last week. 16. His new novel (publish) ...in two months. 17. Nam doesn’t his motorbike today. It (repair) ..right now. 18. A new supermarket (build)... in the neighborhood recently. VI. Choose the correct answer A, B, or C to complete each of the sentences. 1.Alaska is perhaps the most state in the USA. It has over three million lakes. A. puzzling B. festive C. amazing 2.The old tradition of first- footing is still practiced today in .. A. Scottish B. Scots C. Scotland 3.In Canada, the serving of coffee at the end of an evening is a signal that it is time for .. A. visitors B. tourists C holiday makers 4.The Maori in New Zealand greet each other by .. their noses. A. punching B. touching C. blowing 5. Australia is composed of seven .. A. nations B. countries C. states 6.There is a red maple leaf on the of Canada. A. flag B. banner C. money VII. Read the passage and answer these questions below: England is not a large country. No town in England is very far from the sea, and many English families spend their summer holidays at the seaside. There are no high mountains in England, no very long rivers and very large forests. There are many towns in England. No town is very far from another. The English countryside between the towns is like a carpets of many colors. In Spring and summer, the fields, meadows and forests are light green or dark green, and the gardens are green , red, blue, yellow and white with flowers. Questions 1.Is England a large country? .................................................................................................................................................. 2. Where do many English families spend their summer holidays? .................................................................................................................................................. 3. Are there many towns in England? .................................................................................................................................................. 4. What is the English countryside like? .................................................................................................................................................. VI. Read the passage and do the tasks that follow Alaska is perhaps the most amazing state in the USA. It has coastlines facing both the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. This state has an incredible three million lakes. That’s four lakes per person living there. Many cities in Alaska cannot be reached by road, sea, or river. The only way to get in and out is by air, on foot, or by dogsled. That’s why Alaska has the busiest sea airport in the world, Lake Hood Seaplane Base. Nearly two hundred floatplanes take off and land on the water of this airport every day. It is a really fun scene to watch. Alaska is called the land of Midnight Sun because in summer, the sun does not set for nearly three months. But in winter the sun stays almost unseen. All Alaskans take special pride in their beautiful and unique state. 1. Alaska ___________. A. is another name for the USA B. is an island in the Pacific Ocean C. has coastlines facing both the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean 2. Which statement below is NOT CORRECT? A. In Alaska, the number of lakes is bigger than that of people. B. There is one lake for each person living there. C. Alaska has an incredibly high number of
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 de_cuong_on_tap_hoc_ky_2_mon_tieng_anh_lop_8_nam_hoc_2018_20.docx
de_cuong_on_tap_hoc_ky_2_mon_tieng_anh_lop_8_nam_hoc_2018_20.docx





