Đề ôn tập kiểm tra môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 10 - Unit 6: Gender Equality
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Đề ôn tập kiểm tra môn Tiếng Anh Lớp 10 - Unit 6: Gender Equality", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
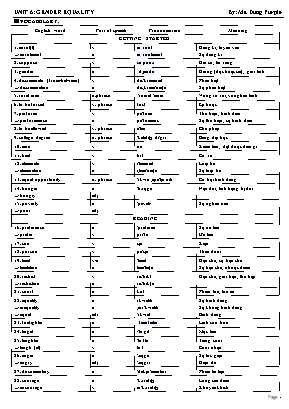
UNIT 6: GENDER EQUALITY By: Ms. Dung Purple þ VOCABULARY: English word Part of speech Pronunciation Meaning GETTING STARTED 1. enrol(l) → enrolment v n ɪnˈroʊl ɪnˈroʊlmənt Đăng kí, tuyển vào Sự đăng kí 2. suppose v səˈpoʊz Giả sử, tin rằng 3. gender n ˈdʒendə Giống (đực hoặc cái), giới tính 4. discriminate (from/between) → discrimination v n dis'krimineit dis,krimi'neiʃn Phân biệt Sự phân biệt 5. rural area n.phrase 'ruərəl 'eəriə Vùng xa xơi, vùng hẻo lánh 6. to be forced v. phrase fɔ:st Ép buộc 7. perform → performance v n pə'fɔ:m pə'fɔ:məns Thể hiện, trình diễn Sự thể hiện, sự trình diễn 8. to be allowed v. phrase ə'lau Cho phép 9. college degree n. phrase 'kɔlidʤ di'gri: Bằng đại học 10. earn v ə:n Kiếm tiền, đạt được điều gì 11. treat v tri:t Cư xử 12. eliminate → elimination v n i'limineit i,limi'neiʃn Loại bỏ Sự loại bỏ 13. equal opportunity n. phrase 'i:kwə ,ɔpə'tju:niti Cơ hội bình đẳng 14. hunger → hungry n adj 'hʌɳgə Nạn đĩi, tình trạng bị đĩi 15. poverty → poor n adj 'pɔvəti/ Sự nghèo nàn READING 16. preference → prefer n v 'prefərən pri'fə: Sự ưu tiên Ưu tiên 17. sue v sju: Kiện 18. pursue v pə'sju: Theo đuổi 19. limit → limitation v/n n 'limit limi'teiʃn Hạn chế, sự hạn chế Sự hạn chế, nhược điểm 20. restrict → restriction v n ris'trikt ris'trikʃn Hạn chế, giới hạn, thu hẹp 21. court n kɔ:t Phiên tịa, tịa án 22. equality → inequality → equal n n adi i:kwɔliti ,ini:'kwɔliti 'i:kwəl Sự bình đẳng Sự khơng bình đẳng Bình đẳng 23. firefighter n ˈfaɪərfaɪtər Lính cứu hỏa 24. target n /'tɑ:git Mục tiêu 25. laughter → laugh (at) n v 'lɑ:ftə lɑ:f Tiếng cười Cười nhạo 26. anger → angry n adj 'ỉɳgə 'ỉɳgri Sự tức giận Giận dữ 27. documentary n 'dɔkju'mentəri Phim tài liệu 28. courage → encourage → encouragement → discourage (from) → discouragement n v v 'kʌridʤ in'kʌridʤ in'kʌridʤmənt dis'kʌridʤ dis'kʌridʤmənt Lịng can đảm Khuyến khích Làm nản chí 29. will n wil Ý chí SPEAKING 30. dependent (on) → dependence → independent → independence adj n adj n di'pendənt di'pendəns ,indi'pendənt ,indi'pendəns Phụ thuộc vào Sự phụ thuộc Độc lập Sự độc lập 31. exhausted = really tired adj ig'zɔ:stid Kiệt sức 32. care -giver n ˈkeəɡɪvə(r) Người chăm sĩc người khác 33. decision-maker n dɪˈsɪʒn meɪkə(r) Người thực hiện các quyết định quan trọng 34. trouble-maker n ˈtrʌblmeɪkə(r) Người gây rắc rối 35. talkative adj 'tɔ:kətiv/ Lắm điều, ba hoa LISTENING 36. wage n weidʤ Tiền cơng (trả theo giờ) 37. salary n 'sỉləri Tiền lương (trả theo tháng) 38. qualified → qualify adj v ˈkwɑːlɪfaɪ 'kwɔlifai Đủ trình độ, đủ năng lực Làm cho đủ phẩm chất, định chất 39. property n property Tài sản, quyền sở hữu 40. address v ə'dres Chăm lo cho một chuyện gì 41. income n 'inkəm Thu nhập WRITING 42. pass down v. phrase Truyền lại điều gì 43. set a good example for v. phrase Làm gương tốt cho ai 44. expense n iks'pens Chi phí, sự tiêu tốn 45. budget n/v 'bʌdʤit Ngân sách/dự thảo ngân sách 46. mature → maturity adj/v n mə'tjuə mə'tjuəriti Chín chắn, trưởng thành Sự chín chắn 47. strength → strengthen n v 'streɳθ 'streɳθən Sức mạnh Làm cho mạnh mẽ 48. weakness → weaken n v 'wi:knis 'wi:kən Điểm yếu Làm cho yếu đi 49. knowledgeable adj 'nɔlidʤəbl Thơng thạo, cĩ kiến thức 50. concentrate (on) → concentration v n 'kɔnsentreit ,kɔnsen'treiʃn Tập trung vào điều gì Sự tập trung 51. family value Giá trị gia đình COMMUNICATION & CULTURE 52. gender gap n. phrase Sự khác biệt/phân biệt về giới tính 53. labor force n. phrase Lực lượng lao động 54. considerable = remarkable → consideration adj n kən'sidərəbl ri'mɑ:kəbl Đáng lưu ý, nổi bật 55. undergraduate n ,ʌndə'grỉdjuit Sinh viên chưa tốt nghiệp ĐH 56. survey n 'sə:vei Cuộc khảo sát 57. be made up of v. phrase Tạo thành 58. challenge n/v 'tʃỉlindʤ Thách thức/sự thử thách 59. domestic violence n. phrase də'mestik 'vaiələns Bạo lực gia đình 60. high-income adj haɪ ˈɪnkəm Thu nhập cao 61. low-paid adj loʊ ˈpeɪd Được trả lương thấp þ LANGUAGE & GRAMMAR: 1. STRESS ON TWO –SYLLABLE WORDS: Dấu nhấn đối với từ cĩ hai âm tiết a- Quy tắc chung: – Hầu hết danh từ và tính từ cĩ 2 âm tiết, trọng âm thường rơi vào âm tiết thứ nhất. E.g. paper [ˈpeɪpə(r)] (giấy) moody [ˈmuːdi] (tâm trạng thất thường) – Phần lớn động từ và giới từ cĩ 2 âm tiết, trọng âm thường rơi vào âm tiết thứ hai. E.g. include [ɪnˈkluːd] (bao gồm) along [əˈlɒŋ] (dọc theo) – Một số trường hợp đặc biệt trong nhấn trọng âm từ cĩ 2 âm tiết: Những từ cĩ tận cùng bằng các hậu tố như -ee, -ese hoặc -oon trọng âm thường rơi vào chính âm tiết đấy. E.g. balloon [bəˈluːn] , Chinese [ˌtʃaɪˈniːz] b- Đổi trọng âm, đổi nghĩa của từ: Trong tiếng Anh, việc thay đổi trọng âm từ cĩ 2 âm tiết đơi khi sẽ ảnh hưởng đến nghĩa của từ đĩ. Dưới đây là 2 trường hợp thường gặp. – Trường hợp 1: Khi trọng âm từ cĩ 2 âm tiết thay đổi, nghĩa chung của chúng được giữ nguyên, nhưng khi trọng âm chuyển từ âm tiết thứ nhất sang âm tiết thứ hai, loại từ chuyển từ danh từ sang động từ E.g. record /ˈrekɔːd/ (n) (bản báo cáo) record /rɪˈkɔːd/ (v) (báo cáo, ghi chép lại) – Trường hợp 2: Khi trọng âm từ cĩ 2 âm tiết thay đổi, nghĩa chung của chúng được giữ nguyên, nhưng khi trọng âm chuyển từ âm tiết thứ nhất sang âm tiết thứ hai, loại từ chuyển từ tính từ sang động từ E.g. perfect /ˈpɜːfɪkt/ (adj) (hồn hảo) perfect /pəˈfekt/ (v) (làm cho hồn hảo, hồn thiện) 2. THE USE OF SOME COMMON MODAL VERBS: Cách dùng của một vài động từ khiếm khuyết phổ biến a. Cách dùng của một vài động từ khiếm khuyết phổ biến Modal verbs Ues Examples 1. CAN - Diễn đạt khả năng ở hiện tại hoặc tương lai. - Diễn tả một sự cho phép. - Diễn tả một sự cấm đốn. - Diễn tả một điều khĩ cĩ thể xảy ra. - I can swim. (khả năng) - You can eat this cake. (Cho phép) - You can’t park here. (cấm đốn) - That can’t be wrong. (khĩ xảy ra) 2. COULD - Diễn đạt khả năng ở quá khứ. - Dùng trong câu điều kiện loại 2. - Diễn tả một yêu cầu lịch sự - He could read when he was 4. (khả năng) - If I were rich, I could fly to the US. (ĐK 2) - Could you please tell me where the nearest bus stop is? (yêu cầu) 3. WILL - Diễn tả sự việc cĩ thể xảy ra trong tương lai - Diễn tả một quyết định ngày lúc nĩi. - Diễn tả một lời hứa - I will go to school tomorrow. (sự việc tương lai) - “Don’t worry. I’ll go home”. (quyết định) - I promise I will be the first in the next semester. (lời hứa) 4. WOULD - Dùng trong câu điều kiện loại 2và loại 3. - Diễn tả một yêu cầu lịch sự. - If I had had a map, I wouldn’t have got lost. - Would you please send me the remote control? 5. MUST - Diễn tả một mệnh lệnh hay một sự bắt buộc. - Diễn tả một dự đốn cĩ cơ sở - Diễn tả một điều ngăn cấm. - You must obey the school’s rules. (bắt buộc) - You worked so hard, you must be tired. (dự đốn) - You mustn’t park here. (cấm đốn) 6. MAY/ MIGHT - Diễn tả một yêu cầu/xin phép lịch sự. - Diễn tả một dự đốn khơng cĩ cơ sở. - May/Might dùng trong câu cảm thán, hay để diễn tả một lời cầu chúc. - May I go out? (xin phép) - She may be in the rơm. I’m not sure (dự đốn) - May everything be okay! (lời chúc) 7. SHOULD - Diễn tả lời khuyên hay ý kiến. - You should lose weight. (lời khuyên) 8. NEEDN’T - Diễn tả sự khơng cần thiết. - Because we have plenty of time we needn’t hurry ** Các hình thức động từ với Modal Verbs: b. PASSIVE VOICE OF MODAL VERBS: Câu bị động của động từ khiếm khuyết þ PRACTICE: EXERCISE 1: Choose the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation 1. A. women B. follow C. concentrate D. project 2. A. address B. allow C. traffic D. rural 3. A. minimum B. influence C. eliminate D. bias 4. A. prevent B. education C. dependent D. eliminate 5. A. encourage B. contribute C. delicious D. college EXERCISE 2: Choose the word that differs from the other three in the position of the primary stress 1. A. career B. gender C. equal D. bias 2. A. enrol B. rural C. allow D. prefer 3. A. abandon B. dependent C. preference D. exhausted 4. A. unequal B. enrolment C. encourage D. minimum 5. A. physically B. equality C. remarkably D. discriminate EXERCISE 3: Fill in each blank with the correct word from the box. Each word has to be used only once. freedom status feminist opportunities education gender quality responsibility injustice women Famous Women Equality Quotes 1. “My goal is not to get a Nobel Peace Prize.... My goal is to get peace and my goal is to see of every child.” (Malala Yousafzai) 2. “ equality is not a woman’s issue, it is a human issue. It affects us all.” 3. “A is anyone who recognizes the equality and full humanity of women and men.” (Gloria Steinem) 4. “To call woman the weaker sex is a libel; it is man’s to woman.” (Mahatma Gandhi) 5. “True equality is not the superiority of women, but the equal of man and woman. (Mercedes Joubert) 6. “ cannot be achieved unless the women have been emancipated from all forms of oppression.” (Nelson Mandela) 7. “As , we must stand up for justice for all.” (Michelle Obama) 8. “Men of respect women’s equality.” 9. “Women are more than 50 percent of the population and more 50 percent of voters. We must demand that we all receive 100 percent of the .” (Beyonce) 10. “Women only have true equality, when men share with them the of bringing up the next generation.” (Ruth Bader Ginsburg) Keys: education gender feminist injustice status freedom women quality opportunities responsibility EXERCISE 4: Fill in each blank with the appropriate form of the word in brackets. 1. Since 2009, Iceland has been the global in gender equality. (lead) 2. For the past five years, Iceland has been in the first rank of educational and in women’s economic conditions. (achieve/ improve) 3. On October 24, 1975, more than 25 thousand women in Iceland took a day off to emphasize the importance of women’s to the economy, both in paid and unpaid work. (contribute) 4. Gender equality is also a part of the to the challenges facing society. (solve) 5. The of women in the labour market in Iceland is one of the highest in the world. (participate) Keys: leader achievement improvement contribution solution participation EXERCISE 5: Read the passage, and decide whether the following statements are true (T), false (F), or not given (NG). Malala Yousafzai was born on July 12, 1997, in Mingora, Pakistan. As a young girl, she demanded that girls should be allowed to receive an education, which resulted in the Taliban issuing a death threat against her. After the Taliban began attacking girls’ schools in Swat, Malala gave a speech whose title was, “How dare the Taliban take away my basic right to education?” In early 2009, Yousafzai began blogging for the BBC about living under the Taliban’s threats to deny her an education. Yousafzai continued to speak out about her right, and the right of all women, to an education. She was shot in the head by a Taliban gunman in 2012, but survived. The shooting resulted in a massive support for Yousafzai, which continued during her recovery. She gave a speech at the United Nations on her 16th birthday, in 2013. She has also written an autobiography “I Am Malala: The Girl Who Stood Up for Education and Was Shot by the Taliban”, which was released in October 2013. At age 17, she became the youngest person to receive the Nobel Peace Prize. In congratulating Yousafzai, U.N. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon described her as “a brave and gentle advocate of peace who through the simple act of going to school became a global teacher”. For her 18th birthday on July 12, 2015, the young activist opened a school for Syrian refugee girls in Lebanon. Its expenses were covered by the Malala Fund, and the school wasdesigned to admit nearly 200 girls from the ages of 14 to 18. “Today on my first day as an adult, on behalf of the world's children, I demand we must invest in books instead of bullets,” Yousafzai spoke in one of the school’s classrooms. T F NG 1. Yousafzai gave many speeches to support girls’ basic right to have o o o education. 2. She was so brave to write articles about the gender discrimination o o o in education in her hometown. 3. She worked as a BBC reporter for a short time. o o o 4. She has worked as a teacher in many countries in the world. o o o 5. She gained great support after being shot nearly dead by Taliban. o o o 6. She was taken to hospital in the capital of Pakistan. o o o 7. She was the youngest person to receive the Nobel Prize. o o o 8. She opened a school for Syrian refugee girls in Lebanon funded o o o by the Malala Fund. 9. She loves peace, and hates war. o o o 10. She founded the Malala Fund. o o o Keys: 1 T 2 T 3 F 4F 5T 6NG 7NG 8T 9T 10NG EXERCISE 6: Complete the conversation between the reporter and Nguyen Thi Hong - Viet Nam’s only female ship’s captain, using the sentences (A-G) given. There are two sentences that you do not need. A. But I quickly cleared such thoughts out of my head and told myself that I had to try or I would feel regret forever. B. I suffered huge losses after several unsuccessful fishing trips. C. Time passed, and I could forecast the weather through clouds, the light of the stars, and the condition of the waves. D. At that time, I was teaching Literature at a middle school, and my aunt passed through my place by boat and asked me to go fishing with her on her ship at sea. E. After five hours of struggling with fierce waves during the night, my crew and I had brought 36 people on board. F. It was a horrible sky, and other boat owners tried their best to escape from the storm. G. My aunt also taught me how to jump from one wave to another and how to manage the ship to follow a school of fish. Reporter: How could you go to sea for the first time? Mrs. Hong: I learned it from my aunt, who was also my first teacher. (1) Reporter: What did you learn from your aunt? She taught me her knowledge of how to watch the stars and manage the ship. (2) Reporter: Your aunt was really a great instructor to you. Mrs. Hong: I think so. (3) Thanks to her, I escaped from death in Typhoon Linda. Reporter: On that fateful night of November 2, 1997, you were the only captain who brought your ship in and also rescued 36 other fishermen. What did you think at that time? Mrs. Hong: I thought I could not survive, so how could I rescue storm victims with my ship? (4) Reporter: How did you and your men rescue others? Mrs. Hong: I told my sailors to throw our two buoys into the sea despite the roaring waves in order to rescue people. (5)_____________________________________________________________________ Keys: 1 D 2 C 3 G 4A 5E EXERCISE 7: The following text is about the advantages of being a working mother. Put the supporting details (A-G) for each benefit in the appropriate gaps. There is an extra. A. Children of working mothers often grow up to be independent, responsible and achievement-orientated. B. She can follow her career, interests, and gain more experiences. C. These children often take on more responsibility, not just because it is expected, but also because it is necessary. D. The family will have more dynamics when both parents go to work. E. As with anything, there will always be advantages and disadvantages with being a working mother. F. Being a mother helps her perform assignments at work with more care and patient. G. The father has to share household chores, and the children understand that a family needs joint effort. Topic sentence: There are several benefits of being a working mother. Supporting idea 1: A working mother brings benefits to her family. 1. 2. Supporting idea 2: A working mother is also beneficial to her children because she sets a good example. 3. 4. Supporting idea 3: Working mothers derive benefits from working, too. 5. 6. Concluding sentence: Obviously, mothers should be strongly encouraged to work outside the home. Keys: 1 D 2 G 3 A 4C 5F 6B EXERCISE 8: Choose the best option to complete the following sentences 1. There are plenty of tomatoes in the fridge. You ______buy any. A. mustn’t B. needn’t C. can’t D. couldn’t 2. It's a hospital. You _______ smoke. A. mustn’t B. needn’t C. can’t D. couldn’t 3. He had been working for more than 11 hours. He ______ be tired after such hard work. He ______ prefer to get some rest. A. should/ might B. can/may C. must/may D. may / might 4. The teacher says we ______ read this book for our own pleasure as it is optional. But we ______ read it if we don't want to. A. can/needn’t B. must/ needn’t C. can/ mustn’t D. needn’t/ can 5. ________ you stand on your head for more than a minute? A. May B. Can C. Might D. Should 7. I wish I ______ buy a new mobile phone but I don’t have enough money. A. can B. will C. may D. could 8. Drivers ______ stop when the traffic lights are red. A. can B. may C. must D. have to 9. ________ I ask a question? -Yes, of course. A. Can B. Could C. Will D. May 10. You _______ take your umbrella. It is not raining. A. mustn’t B. shouldn’t C. needn’t D. can’t 11. Jack ________ come to our wedding, but we aren’t sure. A. may B. will C. can D. must 12. I didn’t feel very well yesterday. I ________ eat anything. A. needn’t B. couldn’t C. mustn’t D. can’t 13. In Korea, many people still feel that women should be in charge of ________after getting married. A. housekeeping B. homemaker C. house husband D. householder 14. The principle of equal pay is that men and women doing_______work should get paid the same amount. A. same B. alike C. similar D. identical 15. In Yemen, women have less________to property ownership, credit, training and employment. A. possibility B. way C. use D. access 16. Women are more likely to be victims of_______violence. A. domestic B. household C. home D. family 17. International Women’s Day is an occasion to make more________towards achieving gender equality. A. movement B. progress C. improvement D. development 18. Reducing gender________improves productivity and economic growth of a nation. A. equality B. inequality C. possibility D. rights 19. Women with high qualifications________to managers. A. must promote B. must be promoted C. must move D. must be moved 20. A common reason that someone__________more for similar work is because of his or her experience or “length of service”. A. may be paid B. should not be paid C. can be paid D. must be paid 21. All forms of discrimination against all women and girls________ immediately everywhere. A. must be taken away B. must be ended C. must be allowed D. must be followed 22. True gender equality ________when both men and women reach a balance between work and family. A. can achieve B. should be achieved C. can be achieved D. should achieve 23. - Nam: “Do you think that there are any jobs which only men or only women can or should do?” - Lan: “____” A. Men are better at certain jobs than women. B. I agree. This really depends on their physical strengths and preferences. C. Women and men should cooperate with each other. D. Men are often favoured in certain jobs. 24. - Lan: “Would you rather work for a male or female boss?” - Nam: “____” A. I’ve been self-employed for five years. B. I don’t like working under time pressure. C. I prefer a male boss. D. I can’t stand the women gossips. 25. - Nam: “Would you rather have a male or a female secretary?” - Lan: “____” A. I want to have a female one. B. The number of female secretaries is increasing. C. The number of female secretaries is staying the same. D. Female secretaries outnumber male ones. Choose the word(s) OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. 26. The gender gap in primary education has been eliminated. A. variety B. inconsistency C. difference D. similarity 27. The United Kingdom has made a remarkable progress in gender equality. A. insignificant B. impressive C. notable D. famous 28. Men and women equally gain first class degrees. A. acquire B. lose C. achieve D. Obtain 29. The United Kingdom still faces challenges in gender equality. A. fairness B. inequality C. evenness D. equilibrium Choose the word(s) CLOSEST in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. 30. This year, more girls enrolled on courses in art and design. A. avoided B. inserted C. erased D. enlisted 31. In some rural areas, women and girls are forced to do most of the housework. A. invited B. encouraged C. made D. contributed 32. Our government has done a lot to eliminate gender inequality. A. cause B. remove C. add D. allow 33. We never allow any kind of discrimination against girls at school. A. approve B. deny C. refuse D. debate 34. Women do not yet have equal rights in the family in this area. A. variable B. similar C. different D. the same EXERCISE 9: Read the passage and choose the correct answer to each of the following questions For Catherine Lumby, deciding to take on the role of breadwinner in her relationship was not a difficult choice. When she discovered she was pregnant with her first child, she had just been offered a demanding new role as Director of the Media and Communications department at the University of Sydney. But she didn't see this as an obstacle, and was prepared to use childcare when the children were old enough. It came, therefore, as a surprise to Lumby and her husband Derek that, after the birth of their son, they couldn’t actually bear the thought of putting him into childcare tor nine hours a day. As she was the one with the secure job, the role of primary care-giver fell to Derek, who was writing scripts for television. This arrangement continued for the next four years, w ith Derek working from home and caring for both of their sons. He returned to full-time work earlier this year. Whilst Lumby and her husband are by no means the only Australians making such a role reversal, research suggests that they are in the minority. In a government-funded survey in 2001, only 5.5 percent of couples in the 30-54 year age group saw the women working either part- or full-time while the men were unemployed. The situation is likely to change, according to the CEO of Relationships Australia, Anne Hollonds. She suggests that this is due to several reasons, including the number of highly educated women in the workforce and changing social patterns and expectations. However, she warns that for couples involved in role-switching, there are many potential difficulties to be overcome. For men whose self-esteem is connected to their jobs and the income it provides to the family, a major change of thinking is required. It also requires women to reassess, particularly with regard to domestic or child-rearing decisions, and they may have to learn to deal with the guilt of not always being there at key times for their children. Being aware of these issues can make operating in non-traditional roles a lot easier. 1. What is the main idea of the passage? A. Men being the bread winners B. Traditional roles of women C. Women being the home makers D. Reversed roles between men and women 2. Catherine and her husband decided that Catherine would be the primary earner because ____. A. she had a badly paid job B. she was not good at childcare C. she had a reliable job D. she wanted her husband to stay at home 3. In paragraph 1, the word “him" refers to ____. A. their son B. her husband C. Derek D. her colleague 4. They decided that Derek would look after their son because they ____. A. couldn’t afford to put their child in care for long periods each day B. didn’t want to put their child in care for long periods each day C. thought childcare was not safe enough for their children D. worried about their son’s health problems 5. In paragraph 2, the word “reversal" is closest in meaning to ____. A. stability B. modification C. rehearsal D. switch 6. One reason for a change in the number of men staying home is ____. A. the stability in the number of highly-educated women who are working B. the fall in the number of highly-educated women who are working C. the rise in the number of highly-educated women who are working D. the fluctuation in the number of highly-educated women who are working EXERCISE 10: Change the following sentences into passive voice 1. You can’t wash this dress " _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. You should open the wine about three hours before you use it. " _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. Members may keeps books for three weeks. After that they must return them. " _____________________________________________________________________________ 4. Passengers shouldn’t throw away their tickets " _____________________________________________________________________________ 5. Visitors must leave umbrellas and sticks in the cloak-room. " _____________________________________________________________________________ 6. You should have taken those books to the library. " _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. We cannot exchange articles bought during the sale. " _____________________________________________________________________________ 8. They ought to have reported the accident to the police. " _____________________________________________________________________________ 9. You mustn’t move this man; he is too ill. " _____________________________________________________________________________ EXERCISE 11: Complete the sentences with must, should, need, needn’t, can, could, may, might 1. In Britain many children ____________ wear uniform when they go to school. 2. That restaurant ______________ be very good. It’s always full of people. 3. I think the government ______________ do more to help homeless people. 4. We have plenty of time for doing the work. We ______________ be hurried. 5. You ______________ ring the bell; I have a key. 6. I ______________ get up early tomorrow. There are a lot of things I want to do. 7. You ______________ explain that again because I understand everything now. 8. I ________________ do that again. It’s my promise. 9. You _____________ take your umbrella along with you today. It ____________ rain later on this afternoon. 10. You _____________ have been absent from that important session. KEYS: 1. must 2. must 3. should 4. needn’t 5. needn’t 6. must 7. needn’t 8. won’t 9. should/may(might) 10. mustn’t EXERCISE 12: Choose the best option to complete the following sentences Young people ______ obey their parents. A. must B. will C. may D. ought to Jenny's engagement ring is enormous! It ______ have cost a fortune. A. should B. will C. might D. must Peter has been working for 10 hours. He ______ be very tired now. A. needn't B. must C. has to D. should I ______ find my own way there. You ______ wait for me. A. should / can't B. have to / must C. can / needn't D. might / mustn't When you have a small child in the house, you ______ leave small objects lying around. Such objects ______ be swallowed, causing serious injury or even death. A. should / must B. should not / might C. needn't / may D. mustn't / can't Those letters ________ now. You can do the typing later. A. need typing B. needn't be typed C. need to type D. needn't typing The museum is open to everybody. It ________ between 9am and 5pm. A. visits B. visited C. can visit D. can be visited The picnic ________ because Peter has just had a traffic accident. A. will cancel B. will be cancelling C. will be cancelled D. will have cancelled The situation ________ to continue. A. cannot allow B. cannot be allowed C. cannot have allowed D. cannot be allowing The machine ________ on by pressing this switch. A. can turn B. can be turned C. must turn D. should be turning Will my car ________ this afternoon? A. fix B. been fixed C. be fixed D. be fixing
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 de_on_tap_kiem_tra_mon_tieng_anh_lop_10_unit_6_gender_equali.docx
de_on_tap_kiem_tra_mon_tieng_anh_lop_10_unit_6_gender_equali.docx





