Bài tập ôn tập Ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh Lớp 6
Bạn đang xem tài liệu "Bài tập ôn tập Ngữ pháp Tiếng Anh Lớp 6", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút DOWNLOAD ở trên
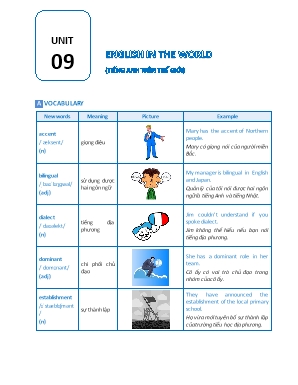
UNIT 09 ENGLISH IN THE WORLD (TIẾNG ANH TRÊN THẾ GIỚI) A VOCABULARY New words Meaning Picture Example accent /ˈỉksent/ (n) giọng điệu Mary has the accent of Northern people. Mary cĩ giọng nĩi của người miền Bắc. bilingual /ˌbaɪˈlɪŋɡwəl/ (adj) sử dụng được hai ngơn ngữ My manager is bilingual in English and Japan. Quản lý của tơi nĩi được hai ngơn ngữ là tiếng Anh và tiếng Nhật. dialect /ˈdaɪəlekt/ (n) tiếng địa phương Jim couldn’t understand if you spoke dialect. Jim khơng thể hiểu nếu bạn nĩi tiếng địa phương. dominant /ˈdɒmɪnənt/ (adj) chi phối chủ đạo She has a dominant role in her team. Cơ ấy cĩ vai trị chủ đạo trong nhĩm của cơ ấy. establishment /ɪˈstỉblɪʃmənt/ (n) sự thành lập They have announced the establishment of the local primary school. Họ vừa mới tuyên bố sự thành lập của trường tiểu học địa phương. flexibility /ˌfleksəˈbɪləti/ (n) tính linh hoạt You shout train your body to develop the flexibility. Bạn nên rèn luyện thân thể để phát triển tính linh hoạt. fluent /ˈfluːənt/ (adj) trơi chảy Most of the students in my class are fluent in English. Hầu hết học sinh trong lớp của tơi đều nĩi tiếng Anh trơi chảy. global /ˈɡləʊbl/ (adj) tồn cầu They are going to hold a conference on global warming. Họ sẽ tổ chức một hội thảo về sự ấm lên tồn cầu. imitate /ˈɪmɪteɪt/ (v) bắt chước Kids are likely to imitate their parents. Trẻ em thường hay bắt chước bố mẹ chúng. intonation /ˌɪntəˈneɪʃn/ (n) ngữ điệu You rise your intonation at the end of some questions. Bạn nâng giọng lên ở cuối một số câu hỏi. look up /lʊk ʌp/ tra cứu I often look up a word in paperback dictionary. Tơi thường tra cứu từ bằng từ điển giấy. mother tongue /ˈmʌðər tʌŋ/ tiếng mẹ đẻ Vietnamese is my mother tongue. Tiếng Việt là tiếng mẹ đẻ của tơi. translate /trỉnsˈleɪt/ (v) dịch I have my assistant translate some documents for me. Tơi nhờ trợ lý dịch vài văn bản cho tơi. variety /vəˈraɪəti/ (n) sự đa dạng, thể loại American English and Canadian English are two varieties of English. Tiếng Anh Mỹ và tiếng Anh Canada là hai loại của tiếng Anh. B GRAMMAR I ƠN TẬP CÂU ĐIỀU KIỆN LOẠI 2 (CONDITIONAL SENTENCES TYPE 2) Chức năng - Dùng để diễn tả điều kiện khơng thể xảy ra ở hiện tại hoặc tương lai, điều kiện chỉ là một giả thiết, một ước muốn trái ngược với thực trạng hiện tại. - Dùng để đưa ra lời khuyên. Cấu trúc If + S + V-ed + (bổ ngữ), S + would + V nguyên mẫu + (bổ ngữ). (Thì Quá khứ đơn) ð Mệnh đề IF dùng thì quá khứ đơn, mệnh đề chính dùng động từ khuyết thiếu “would + V” Ví dụ If I were a bird, I would be very happy. (Nếu tơi là một con chim, tơi sẽ rất hạnh phúc) → tơi khơng thể là chim được. If I had a million USD, I would buy that car. (Nếu tơi cĩ một triệu đơ la, tơi sẽ mua chiếc xe đĩ.) → hiện tại tơi khơng cps. Lưu ý - Trong câu điều kiện loại 2, ở mệnh đề “IF”, với chủ ngữ “I/ he/ she/ It” ta cĩ thể dùng “were” hoặc “was” đều được. (were được dùng trong tình huống trang trọng hơn.) - Ta cũng cĩ thể dùng “could” hoặc “might’’ trong mệnh đề chính. WOULD = sẽ (dạng quá khứ của WILL) COULD = cĩ thể (dạng quá khứ của CAN) MIGHT = cĩ thể (dạng quá khứ của MAY). n BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN Bài 1: Nối các câu ở cột A với cột B sao cho phù hợp. Cột A Cột B 1. If I had Laura’s phone number now, 2. If it was sunny and hot today, 3. Mike would invite you to his next party 4. If I had wings, 5. You would get better grades 6. If I were in your position, 7. We could take photos here 8. If I lived in a developed country, 9. If I were a governor for only a day, 10. Mike wouldn’t have such family problems. a. I would think twice before I drop out of school. b. I would forbid smoking everywhere in the state. c. we would take the kid for a swim in the beach. d. if his parents weren’t drug addicts. e. if you were one of his friends. f. I would send her an urgent SMS. g. I would find a well-paid job easily. h. I would fly back home to see my wife and kids. i. if it wasn’t forbidden to do so. j. if you worked hard. 1. ________ 2. ________ 3. ________ 4. ________ 5. ________ 6. ________ 7. ________ 8. ________ 9. ________ 10. ________ Bài 2: Hồn thành câu điều kiện loại 2 dưới đây. 1. If I ___________ (be) you, I would practice more often for the upcoming test. 2. I ___________ (spend) a lot of money if I won the lottery. 3. What ___________ (you/do) if I gave you one million dollars? 4. If I met Rihanna, I ___________ (say) hallo. 5. I would take the underground every day, if I ___________ (live) in London. 6. You would feel a lot better, if you ___________ (not/smoke) so much. 7. If I ___________ (be) you, I would follow your mum’s advice. 8. I would run away if I ___________ (see) a ghost. 9. If I were you, I ___________ (accept) the offer. 10. If you ___________ (have to) choose a place to live, which one would you choose? 11. What would you do if you ___________ (see) a robbery? Bài 3: Cho dạng đúng của động từ trong ngoặc để hồn thành các câu điều kiện loại 1 và loại 2 dưới đây. 1. If I were you, I (learn) ______________ now. 2. If Chuck ______________ (ask) us, we would lend him our books. 3. If they ______________ (be) at home, they will learn my words. 4. If Jack has a new DVD, he ______________ (lend) it to Cindy. 5. If Bill washed the car, he ______________ (get) more pocket money. 6. If you ______________ (come), you would meet them. 7. If we go to London, we ______________ (see) Buckingham Palace. 8. Jenny will help you if she ______________ (have) more time. 9. Sandy ______________ (tell) him If he asked her. 10. I ______________ (wash) my hands if he gives me the soap. 11. If the g hosts passes through the door, she ______________ (scream). 12. If we ______________ (swim) a lot, we would win the competition. 13. The Zongs will travel to the USA if they ______________ (win) in the lottery. 14. If you ______________ (run), you would catch the bus. 15. If Tessy has enough money, she ______________ (buy) some dresses. II MỆNH ĐỀ QUAN HỆ (RELATIVE CLAUSE) 1. Định nghĩa Mệnh đề quan hệ (MĐQH) Định nghĩa - Mệnh đề quan hệ (Mệnh đề tính từ) là một loại mệnh đề phụ thuộc được bắt đầu bằng các Đại từ quan hệ: who, whom, which, that, whose hay những trạng từ quan hệ: why, where, when. - Mệnh đề quan hệ dùng để bổ nghĩa cho danh từ đứng trước nĩ trong mệnh đề chính của câu hay để chỉ rõ người/ vật cụ thể đang được nĩi đến. Ví dụ I told you about the woman who lives next door. (Tơi đã nĩi với bạn về người phụ nữ sống cạnh nhà.) 2. Các loại Đại từ quan hệ Đại từ Cách dùng Ví dụ WHO - Thay thế cho danh từ chỉ người đứng trước nĩ - Làm Chủ ngữ trong mệnh đề quan hệ (MĐQH). ...N (person) + WHO + V + 0 - Làm Tân ngữ cho động từ trong MĐQH. ... N (person) + WHO + S + V The girl who is standing there is Ann. The student who the head teacher met was John. WHOM - Thay thế cho danh từ chỉ người, làm tân ngữ cho động từ trong MĐQH. ...N (person) + WHOM + S + V - Chú ý: “who” cĩ thể thay thế cho “whom”, nhưng “whom” KHƠNG THỂ thay thế cho “who”. Is she the girl whom you are waiting for? Is she the girl whom is waiting for you? → SAl → Is she the girl who is waiting for you? → ĐÚNG WHICH - Thay thế cho danh từ chỉ Vật - Làm Chủ ngữ hoặc Tân ngữ trong mệnh đề quan hệ. ...N (thing) + WHICH + V + O ...N(thing) + WHICH + S + V The book which is on the table is mine. The dress which she is wearing is beautiful. THAT Cĩ thể thay thế cho vị trí của who, whom, which, That ≈ Who / Whom / Which The pen that/which is on the desk is expensive. The dancers that/who/whom he painted were very lively. WHOSE - Dùng để chỉ sở hữu cho danh từ chỉ người hoặc vật, thường thay cho các tính từ sở hữu: her, his, their,... hoặc hình thức sở hữu cách ’s. ...N (person, thing) + WHOSE + N + V.... - Chú ý: Whose chỉ đứng giữa hai danh từ. Whose khơng đứng trước Động từ trong MĐQH. The dog whose hair is brown belongs to me. 3. Các loại trạng từ quan hệ Trạng từ Cách dùng Ví dụ WHY - Mở đầu cho mệnh đề quan hệ chỉ lý do, thường thay cho cụm “for the reason, for that reason”. ...N (reason) + WHY + S + V ... I don’t know the reason. You didn’t go to school for that reason. → I don’t know the reason why you didn’t on to school. WHERE - Thay thế từ chỉ nơi chốn như “place, house, street, town, country...” thường thay cho “there”. ....N (place) + WHERE + S + V... (WHERE = ON / IN / AT + WHICH) The hotel wasn’t very clean. We stayed at that hotel. → The hotel where we stayed wasn’t very clean. = The hotel at which we stayed wasn’t very clean./The hotel which we stayed at was very clean. WHEN - Thay thế từ chỉ thời gian như “time, moment day, period, summer...” thường thay cho từ “then”. ...N (time) +WHEN + S + V... (WHEN = ON / IN / AT + WHICH) - I don’t know the time. She will come back then. → I don’t know the time when she will come back. - Do you still remember the day? We first met on that day. → Do you still remember the day when we first met? - Do you still remember the day on which we first met./ Do you still remember the day which we first met on? 4. Giới từ trong Mệnh đề quan hệ Cách dùng Ví dụ Nếu trong Mệnh đề quan hệ cĩ giới từ thì giới từ cĩ thể đặt trước hoặc sau mệnh đề quan hệ (chỉ áp dụng với whom và which.) Mr. Brown is a nice teacher. We studied with him last year. → Mr. Brown, with whom we studied last year, is a nice teacher. → Mr. Brown, whom we studied with last year, is a nice teacher. Nếu Mệnh đề quan hệ bắt đầu bằng đại từ quan hệ “who, that” giới từ buộc phải đặt sau, KHƠNG đặt trước The playground wasn’t used by those children that it was built for. → ĐÚNG The playground wasn’t used by those children for that it was built → SAI n BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN Bài 4: Điền vào chỗ trống “who” hoặc “which”. 1. A soldier is someone ___________ works In the army. 2. A student is a person ___________ goes to school. 3. An ostrich is a bird ___________ cannot fly. 4. A cook is someone ___________ makes meals at a restaurant. 5. A tire is a thing ___________ you can find on a wheel. 6, A stick is a piece of wood ___________ is long and thin. Bài 5: Dùng “that” hoặc “whose” để nối các câu dưới đây. 1. I admired the stuntman. His part was so dangerous. I admired the stuntman 2. We ate the cake. It was on the cupboard. We ate the cake 3. She found the bag. It belonged to her. She found the bag 4. Can you see the car? Its door is scratched. Can you see the car ? 5. You are the partner. I want to work with you. You are the partner 6. I couldn’t help the students. Their tests were a failure. I couldn’t help the students 7. This is the guy. I get it from him. This is the guy 8. I like the house. Its roof was made of red ties. I like the house 9. A spade is a tool. You dig with it. A spade is a tool 10. Here is the museum. I told you about it. Here is the museum 11. I can’t respect politicians. Their only ambition is to be in power. I can’t respect politicians 12. This is the man. We bought the ring from him. This is the man 13. We can’t afford new cars. Their price is too high. We can’t afford new cars 14. Where is the cassette? We listened to it. Where is the cassette ? 15. The film is about a king. His brother kills him. The film is about a king 16. I met some people. Their houses were badly damaged. I met some people Bài 6: Điền vào chỗ trống các đại từ và trạng từ quan hệ “who, whom, which, whose, where, when” sao cho thích hợp. 1. Can you give me back the money ________ I lent you last month? 2. This is the restaurant ________ we used to eat when we lived in Boston. 3. Mark has sent me an e-mail ________ l haven’t replied yet. 4. Who’s the person ________ is sitting next to Nancy? 5. They complained about the wrong goods ________ were sent to them. 6. This is Susan ________ husband works in the sales department 7. Candy is wearing a new dress ________ she bought in the summer sales. 8. Monday is the day ________ bills have to be paid. 9. The secretary showed me the filing cabinet ________ important documents are filed. 10. Do you like the boy ________ Mary is talking to? 11. We enjoyed the party ________ Peter and Pam had to celebrate Christmas. 12. Are you the person ________ applied for a job as a receptionist? 13. Is this the pub ________ you meet your friends? 14. You have to delete the sheet ________ is repeated. 15. April is the month ________ we have Easter holiday in Spain. 16. The advice ________ Sam gave me was quite senseless. 17. Have you bought the food ________ I asked you? 18. Phone Mrs Smith ________ you will have to talk to tomorrow. 19. Let’s visit the park ________ we played after school. 20. Celebrities receive lots of invitations ________ they don’t accept. 21. Did you refuse the offer ________ the company made you? n BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN Bài 7: Cho dạng đúng của động từ trong ngoặc để hồn thiện câu điều kiện loại 1 và loại 2. 1. If I ______________ (see) John. I ______________ (tell) him your news. 2. You ______________ (meet) my brother if you ______________ (go) to town on Monday. 3. Meg sleeps only 5 hours a day. If she ____________ (sleep) longer, her health ___________ (improve) fast. 4. If she _____________ (want) to talk to me, she ____________ (ring up). I guess she doesn’t. 5. If you ______________ (need) help, my father ______________ (help) you. 6. We ______________ (have) a picnic if the day ______________ (be) fine. 7. I ______________ (understand) Mr. Brown if he ______________ (speak) slowly. 8. If you ______________ (see) a policeman, he ______________ (show) you the way. 9. I ______________ (finish) the job tomorrow if I ______________ (can). 10. If you ______________ (give) him good meals, he ______________ (not be able) to work hard. He would be too lazy to work then. 11. You ______________ (make) a fortune if you ______________ (take) my advice. Too bad! 12. I ______________ (not need) an umbrella if it ______________ (not rain). 13. If she ______________ (think) it over carefully, she ______________ (form) a clear opinion. 14. If she ______________ (catch) a bus now, they ______________ (arrive) at half past nine. 15. He _____________ (find) the answers if he _____________ (look) at the back of the book. 16. If I ______________ (think) that about him. I ______________ (say) so aloud. 17. If he ___________ (promise) to behave in the future, his mum ___________ (forgive) him. 18. If you ______________ (want) me to, I ______________ (come) for a walk with you. 19. If we _____________ (can) come on Sunday, we _____________ (come). I am really sorry. 20. If you _____________ (wait) for a moment, the waiter _____________ (bring) you a coffee. 21. He ______________ (lose) weight if he ______________ (stop) eating so much. 22. Life ______________ (be) monotonous if we ______________ (have) nothing to do. 23. He ______________ (not phone) me here unless it ______________ (be) urgent. 24. If they ______________ (love) each other, they ______________ (not fight) so much. 25. If she ______________ (be) patient, l ______________ (try) to explain. 26. If he ______________ (do) that again, his father ______________ (punish) him. 27. If Peter ______________ (ask) Marry, I’m sure she ______________ (marry) him. 28. She ______________ (get) fit if she ______________ (walk) every day 3 km. 29. If she ______________ (drink) this medicine, she ______________ (feel) much better. 30. He ______________ (be) very pleased if it ______________ (be) really true. Bài 8: Viết lại các cặp câu dưới dây thành câu cĩ chứa mệnh đề quan hệ. 1. She worked for a man. The man used to be an athlete. 2. They called a lawyer. The lawyer lived nearby. 3. I sent an email to my brother. My brother lives in Australia. 4. The customer liked the waitress. The waitress was very friendly. 5. We broke the computer. The computer belonged to my father. 6. I dropped a glass. The glass was new. 7. She loves books. The books have happy endings. 8. They live in a city. The city is in the north of England. 9. The man is in the garden. The man is wearing a blue jumper. 10. The girl works in a bank. The girl is from India. 11. My sister has three children. My sister lives in Australia. 12. The waiter was rude. The waiter was wearing a blue shirt. 13. The money is in the kitchen. The money belongs to John. 14. The table got broken. The table was my grandmother’s. 15. The television was stolen. The television was bought 20 years ago. 16. The fruit is on the table. The fruit isn’t fresh. Bài 9: Chọn từ thích hợp điền vào chỗ trống. bowl call come dress eat give lived make name peel play see throw windows October 31st is Halloween. On this day children in Britain and USA (1) _________ up as witches and ghosts. They also (2) ________ lamps out of pumpkins and put them in the (3) _________. Then they go to the people’s doors. They (4) _________ out: ‘Trick or treat.” When people don’t (5) _________ them a treat they play a trick on them. There also Halloween parties where they (6) _________ games. Such a game is “apples on the string” where people have to (7) _________ apples hanging from a string without using their hands. Another game is “bobbing the apple”. There you have to get apples out of a (8) _________ without using your hands. A third game is “fortune telling”. Therefore you have to (9) _________ an apple and (10) _________ the long peel over your shoulder. Then look at the peel and try to (11) _________ a letter. This is the first letter of the person’s (12) _________ you are going to marry. Halloween goes back many years when the Celts (13) _________ in England. They thought that at this night the ghosts of the dead (14) _________ back. Bài 10: Đọc đoạn văn dưới đây và trả lời câu hỏi. East Somalia’s prolonged shortage of rain, which has already caused food supplies to fail and brought unemployment in farming areas, could also affect the production of electricity, and thus reduce the output from the nation’s mines. The mining industry, and especially copper mining, uses a huge amount of electricity and is almost completely dependent on the government Electricity Supply Commission. But the Commission has recently asked the mines what would happen if electricity supplies were reduced by ten, twenty or thirty percent. The Commission’s power stations, which produce the electricity using coal as fuel, are mostly situated near the large coalfields of Eastern Province. But this area has little water so the cooling towers at the power stations have to be supplied with water from elsewhere. The problem now is that water levels in all rivers and lakes have fallen dangerously low and, in some cases, are well below the intake pipes which feed into the pipelines which supply the cooling towers. In a desperate attempt to solve the problem, engineers are spending some forty million dollars on building a series of small dams across the Haro River. It is hoped that these dams will make the water level at the Malawa Dam rise so that water can then be pumped through a new pipeline to the power stations. This will take time and It is now the dry season. Very little rain falls before October or November, and, after a shortage which has lasted for four years and is believed to be the worst in two centuries, nobody can say whether the rains will be sufficient. The amount of electricity and water used by the mines has tended to increase in recent years. The mines, which produce about half the country’s export earnings, need electricity in order to pump fresh air through their workings and to drive machines which crush vast quantities of rock. Each mine also has to provide accommodation for as many as three thousand workers. 1. How might West Somalia’s Jack of rain affect electricity Supplies and mining? A. Copper mines are having to use less electricity. B. Coal supplies are failing to reach power stations. C. Electricity supplies to mines may be cut by up to thirty percent. D. Copper mines may be unable to pump water by October. 2. Where does the Electricity Supply Commission produce most of its electricity? A. Along the Haro River B. Near the copper mines C. At the Malawa Dam D. In Eastern Province 3. The action that the engineers are taking A. may not help If there is sufficient rain. B. will become effective towards the end of the year. C. should get enough water to the mines. D. will use up a lot of electricity. 4. The engineers aim to A. change the direction of the Haro River. B. keep more water at the Malawa Dam. C. get more water into the Haro River. D. dig out artificial lakes near the dam. 5. Why are the copper mines important to East Somalia? A. They train many skilled mechanics. B. Each mine employs approximately 3,000 people. C. Their costs and production are rising. D. They bring in fifty percent of what the country earns.
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 bai_tap_on_tap_ngu_phap_tieng_anh_lop_6.docx
bai_tap_on_tap_ngu_phap_tieng_anh_lop_6.docx





